Interface Basics
BuildNinja's user interface is designed to provide quick access to all core features, from managing projects and viewing builds to configuring projects and deployments. Familiarity with the layout will help you work more efficiently and reduce the time spent searching for tools or settings.
Sidebar
Sidebar serves as the primary navigation menu within the BuildNinja. It is typically anchored to the left side of the interface and provides persistent access to core features. The Sidebar includes the following key sections:
- Dashboard: Overview of recent build and deployment activity.
- Projects: Manage project-specific and build configuration settings.
- Agents: Monitor and manage build agents available to execute builds.
- Queue: View and manage builds waiting to be executed, including their priority and assigned agents.
- Trigger: Configure external or manual triggers for build execution.
- Users: Manage user accounts and access permissions.
- Settings: Configure system-wide settings such as SSO integrations.
- Expand/Collapse Toggle: Show or hide the project management tree from any page for quick access and navigation.
Dashboard
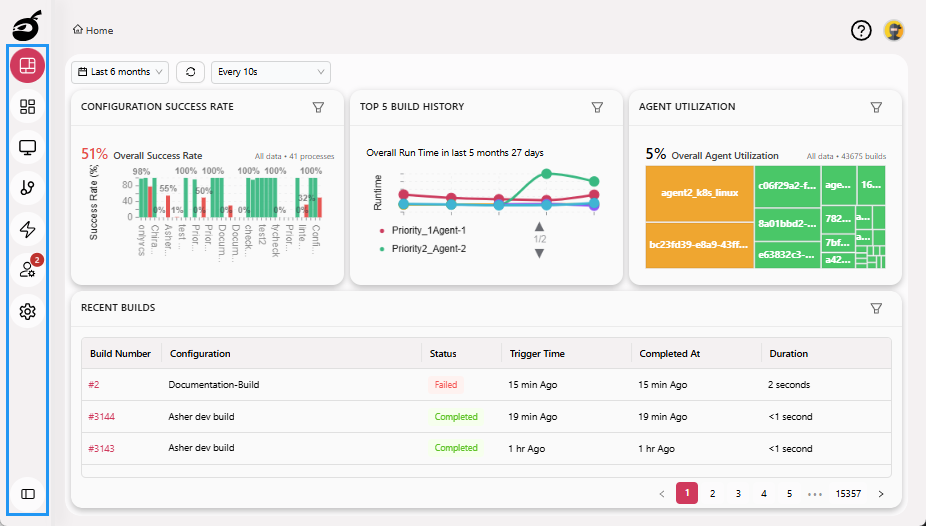
Dashboard provides a centralized summary of BuildNinja's current state. It offers real-time indicators that help you monitor overall system and project performance at a glance.
Dashboard Controls
Time Range Filter
Customize the data shown on the dashboard by selecting a predefined time range:
- Last 24 hours
- Last 7 days (Week)
- Last 30 days (Month)
- Last 90 days (Quarter)
- Last 6 months
- Last 1 year
- Last 3 years
Refresh Options
- Manual Refresh: Click Refresh button to instantly update the dashboard with the latest data.
- Auto Refresh: Enable or disable auto-refresh with the following interval options:
- Every 10 seconds
- Every 30 seconds
- Every 1 minute
- Every 5 minutes
- Select Auto Refresh: Off to disable automatic updates
Key Metrics
The dashboard provides detailed metrics and filters to help you assess and optimize your CI/CD builds:
- Configuration Success Rate: See the percentage of successful builds for each configuration.
- Top 5 Build History: Highlights the five most recent builds with their outcomes.
- Agent Utilization: Understand how efficiently your build agents are being used over time.
Recent Builds
The Recent Builds section displays the latest build activity across your projects. Each entry includes:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Build Number | Unique identifier for the build |
| Configuration | The associated build configuration |
| Status | Build result |
| Trigger Time | When the build is scheduled to run on the agent; it includes the queue time also |
| Completed At | When the build finished |
| Duration | Total time the build took to complete |
This table helps you quickly identify build status and troubleshoot issues when needed.
Projects
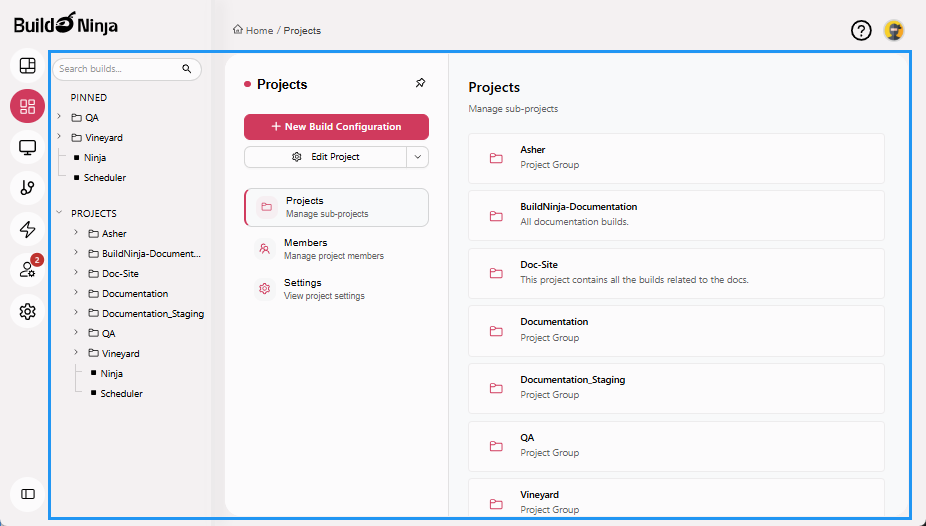
Projects organizes individual projects, each serving as a container for related sub-projects and build configurations. Within Projects, you can:
- View a list of active projects and sub-projects
- Add, copy, and delete projects
- Add and view build configurations
- Pin frequently accessed projects and build configurations
- Manage user access to projects and build configurations
- Define and manage build parameters
Each project serves as a container for its build configurations, execution history, and related records.
Projects Tabs
The following tabs are available to help you manage and configure projects:
-
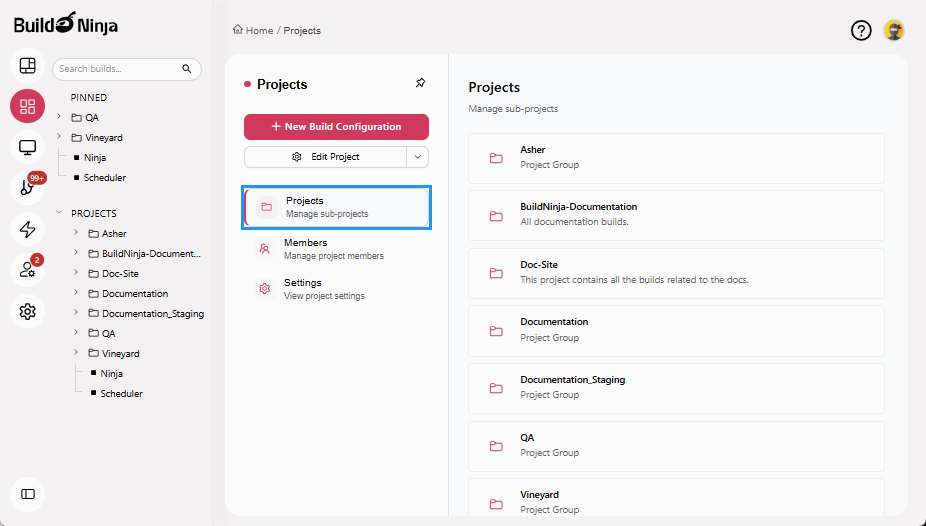
Projects: Organizes projects, sub-projects, and build configurations in a hierarchical structure. You can create, copy, delete, and pin projects, as well as add and view build configurations.
-
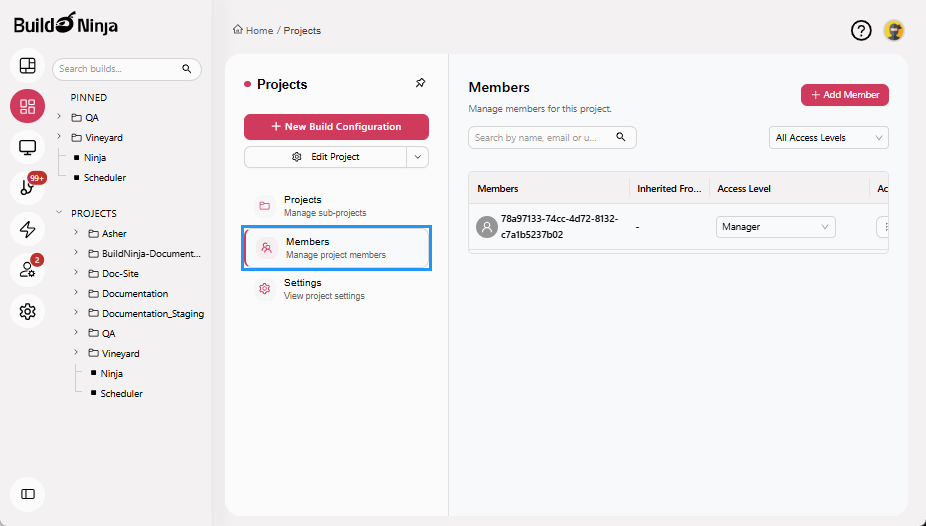
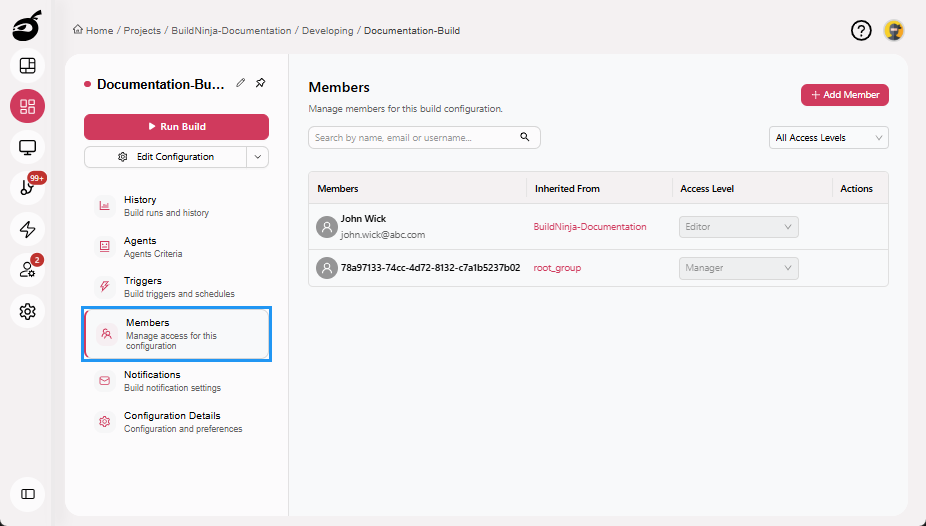
Members: Controls user access to projects and build configurations using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). You can add users, assign roles, and manage permissions at the project level.
-
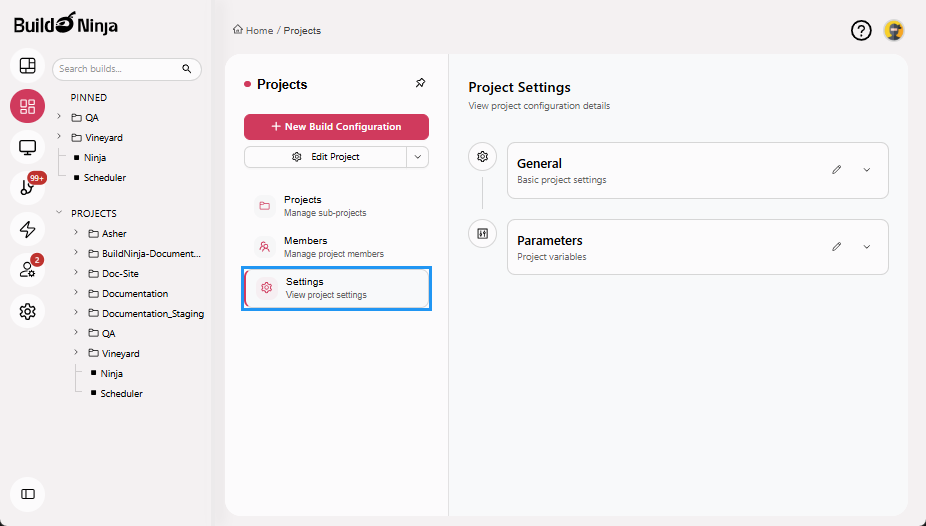
Settings: Provides access to project-level configuration options.
Projects Settings Tabs
The following tabs are available to help you manage project settings:
-
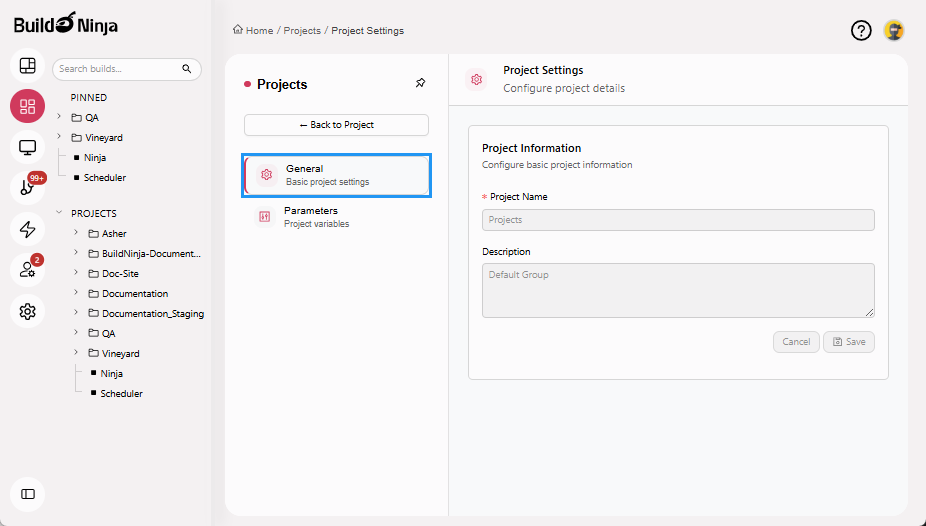
General: Allows you to update the project name and description.
-
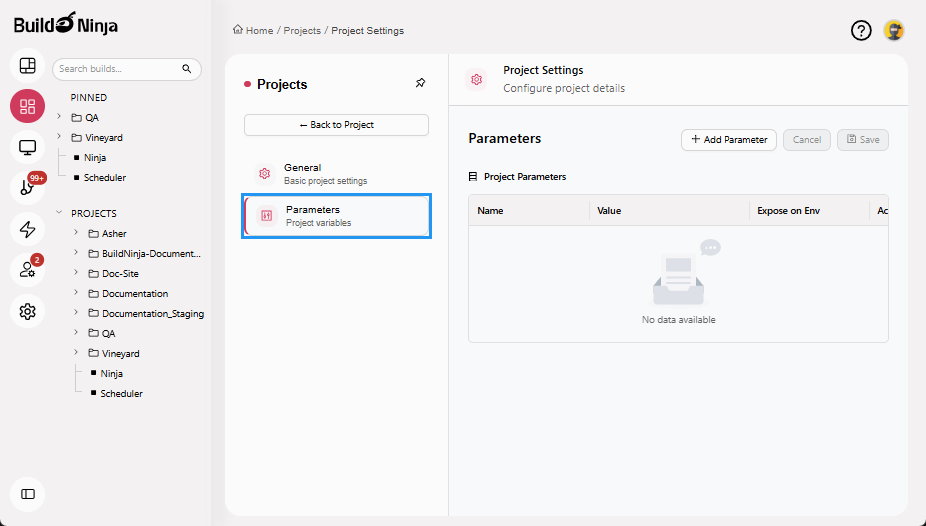
Parameters: Allows you to define and manage build parameters used by build configurations within the project.
Build
Build provides detailed insight into individual build processes, allowing you to manage, monitor, and troubleshoot builds effectively. It enables you to:
- Browse the history of past builds
- View logs for each step in the build process
- Check and update configuration details
- Define and manage build parameters to customize build behavior
- Identify and troubleshoot build failures
- Download build artifacts
- View compatible agents for the build
- Configure triggers to automate build execution
- Manage user access to the build using RBAC
- Manually run builds when needed
Build Tabs
The following tabs are available to help you interact with and configure builds:
-
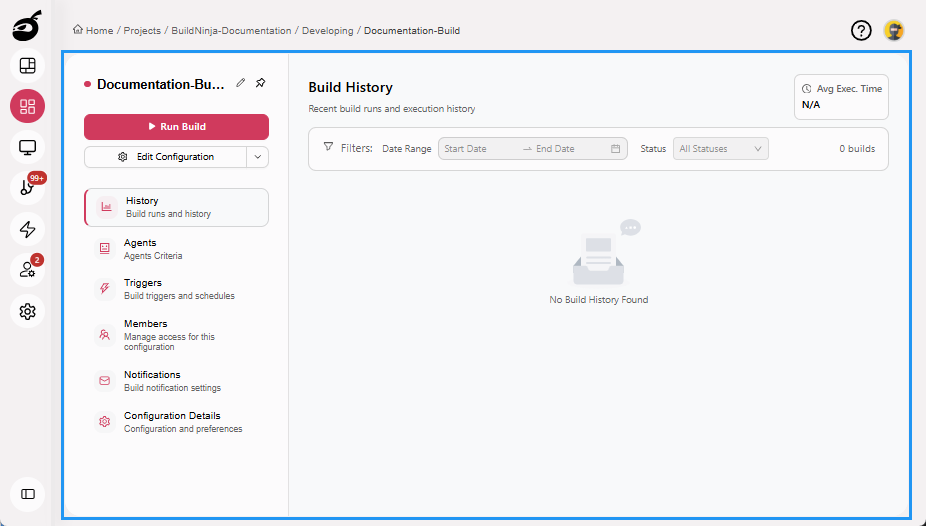
History: Displays high-level build information, including status, trigger time, and duration.
-
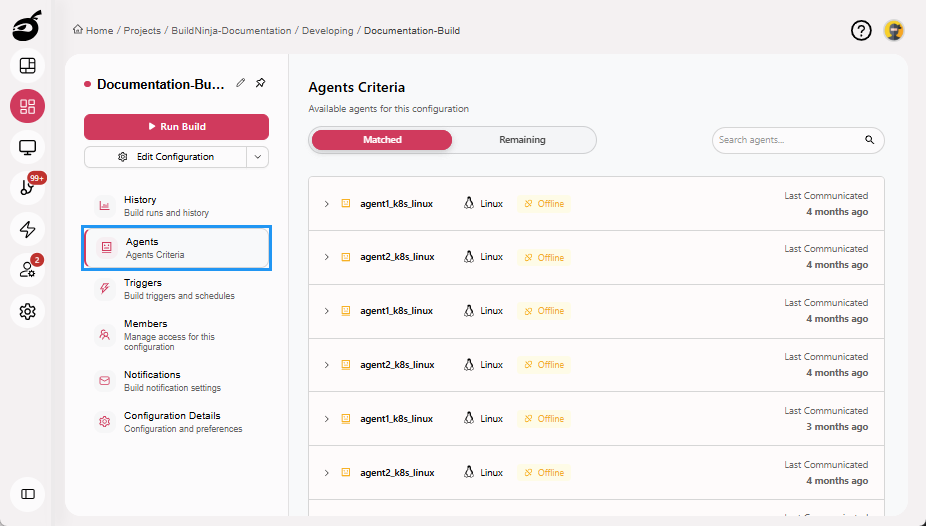
Agents: Lists available build agents capable of running the build, based on platform, capacity, and configuration.
-
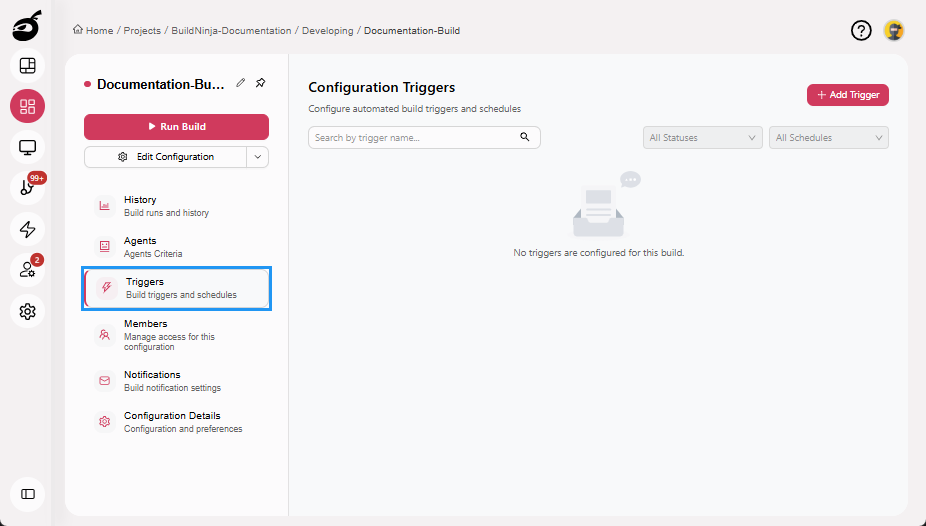
Triggers: Allows you to define when builds should be triggered.
-
Members: Controls user access to the build configuration using RBAC. You can add users, assign roles, and manage permissions specific to the build configuration.
-
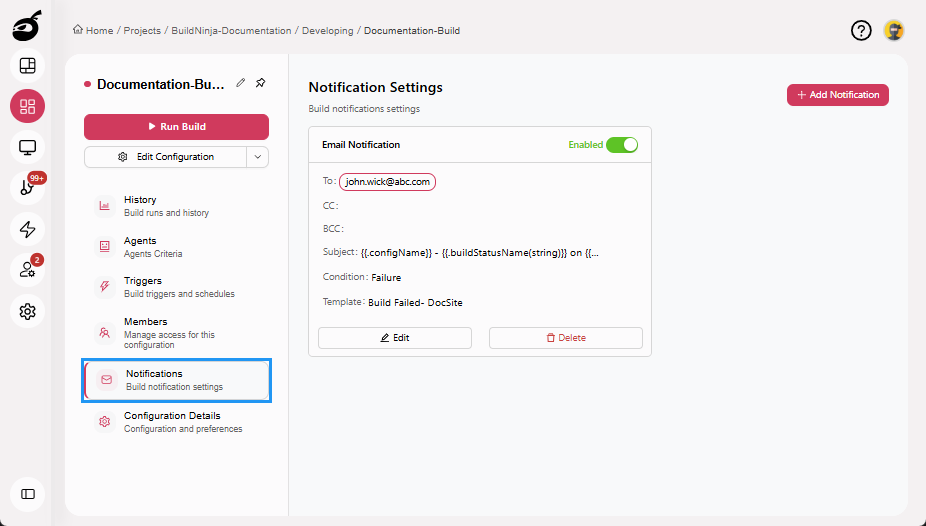
Notifications: Allows you to define how and when you receive alerts for your builds.
-
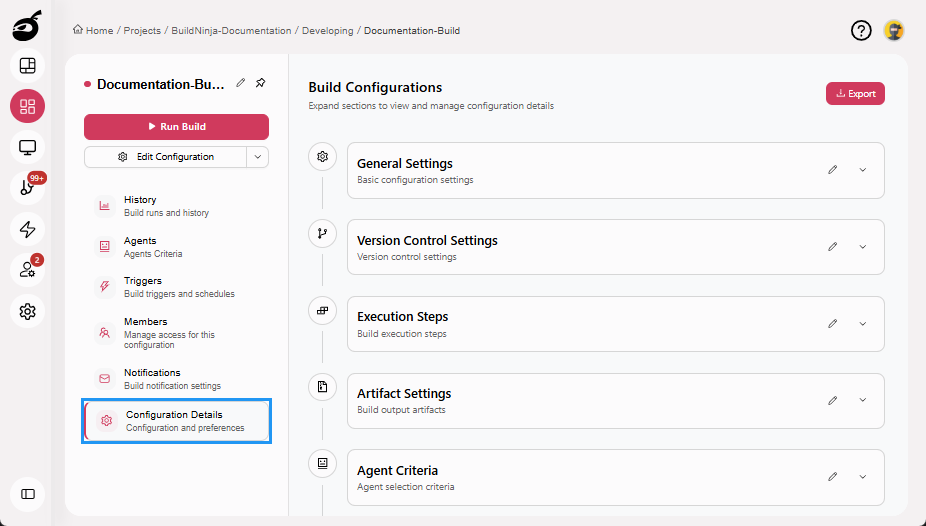
Configuration Details: Provides access to the build’s configuration options, such as repository settings, execution steps, artifacts settings, and agent criteria.
Build Result Tabs
The following tabs are available to view build results that provide detailed insights into each successful or failed build:
-
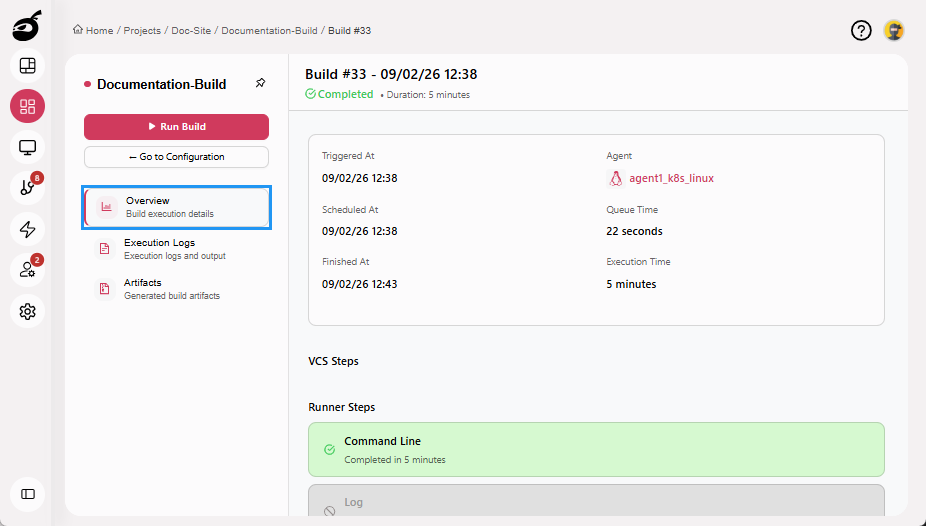
Overview: Displays key details such as trigger information, build duration, and agent details.
-
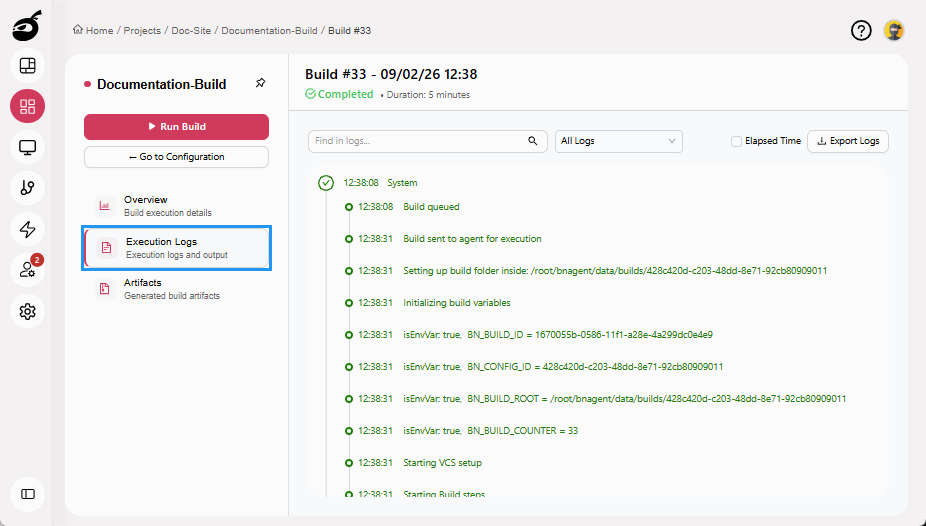
Execution Logs: Provides a step-by-step record of the build process, useful for reviewing executed actions and diagnosing errors.
-
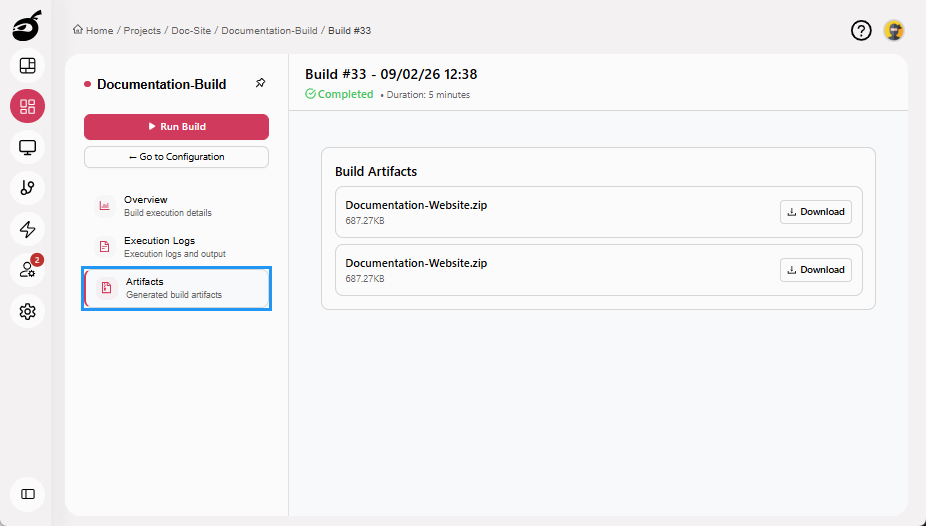
Artifacts: Lists the files generated during the build, if artifact publishing is configured.
Build Configuration Tabs
The following tabs are available to configure and manage your build settings and requirements:
-
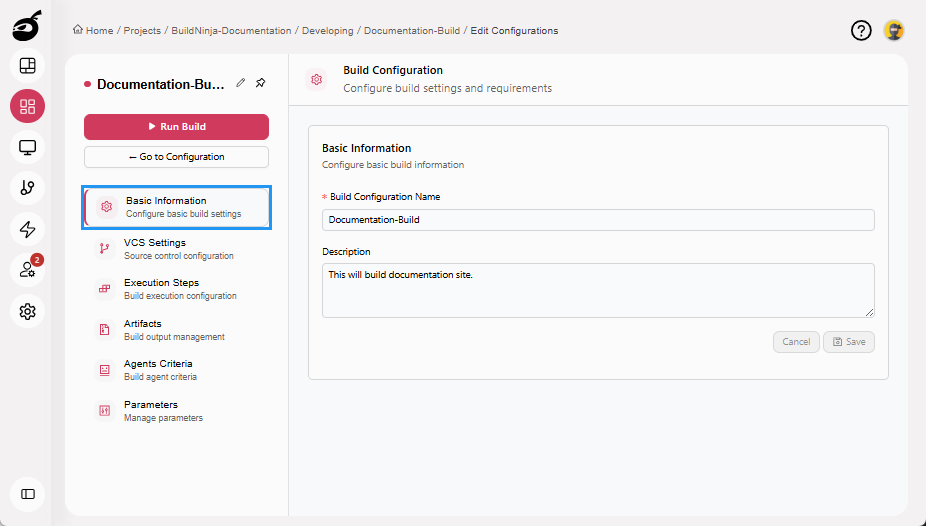
Basic Information: Manage the build name and description.
-
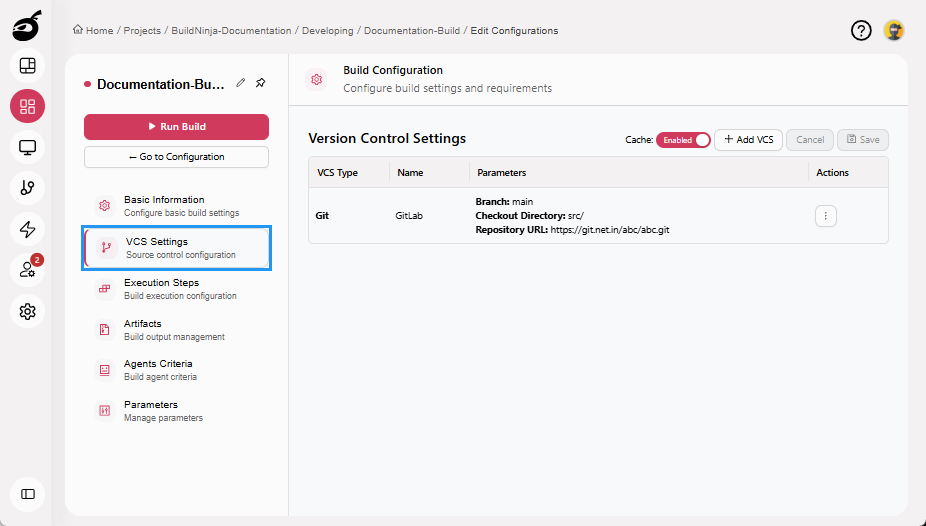
VCS Settings: Configure version control repositories and caching.
-
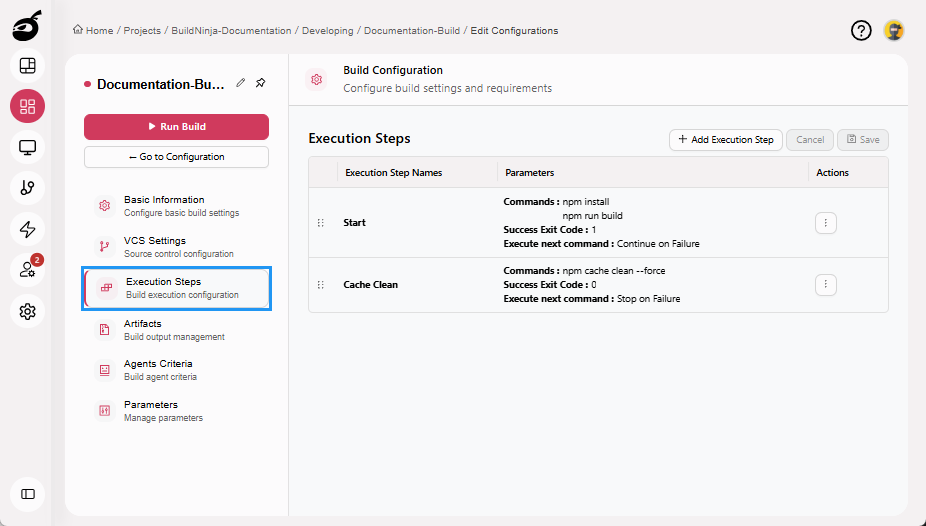
Execution Steps: Define the sequence of actions for building, testing, and deploying code.
-
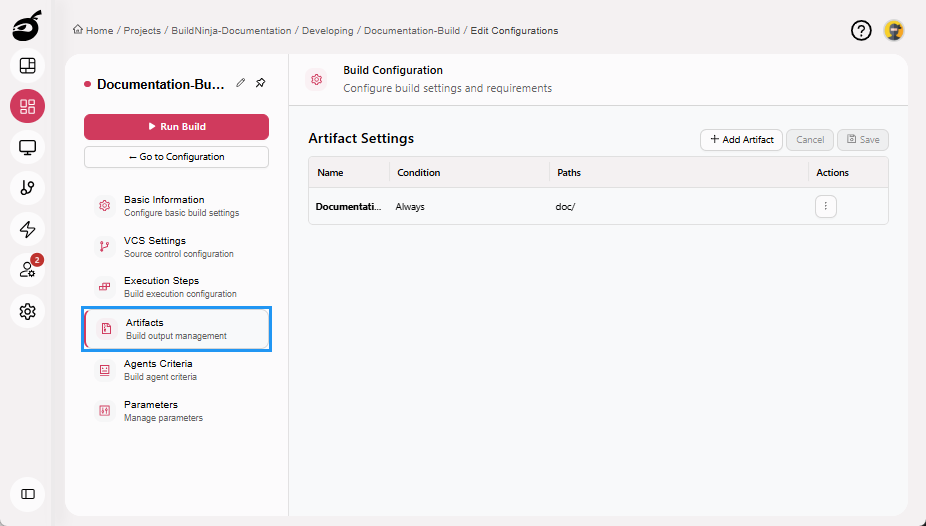
Artifacts: Specify the directories where build artifacts will be stored after the build process completes.
-
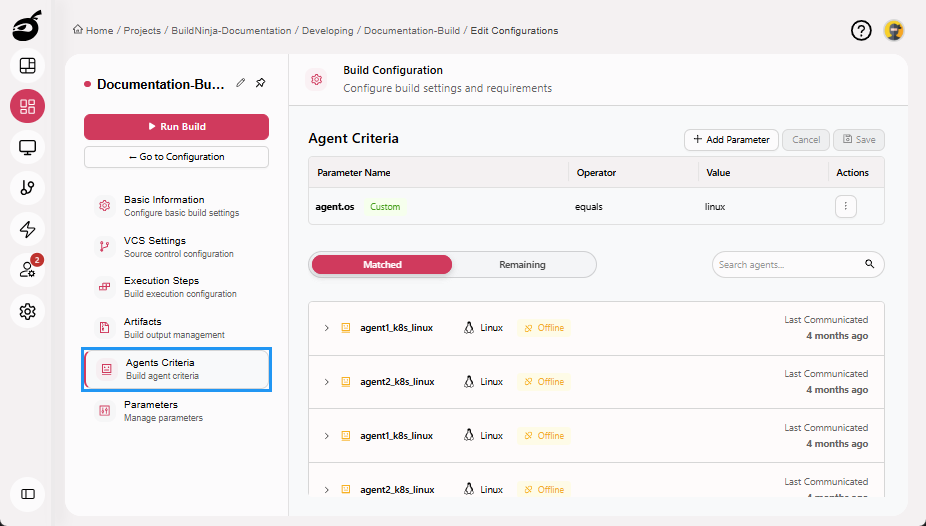
Agents Criteria: Set rules to select suitable build agents based on OS, tools, or tags.
-
Parameters: Define and manage build parameters that can be used within the build configuration. These parameters allow you to customize build behavior and reuse values across execution steps.
Build Runners
Build RunnersBuild Runners define how a build step is executed inside BuildNinja. Each runner encapsulates a specific execution strategy — such as running shell commands, building . define how your execution steps are executed. BuildNinja supports the following runner types:
-
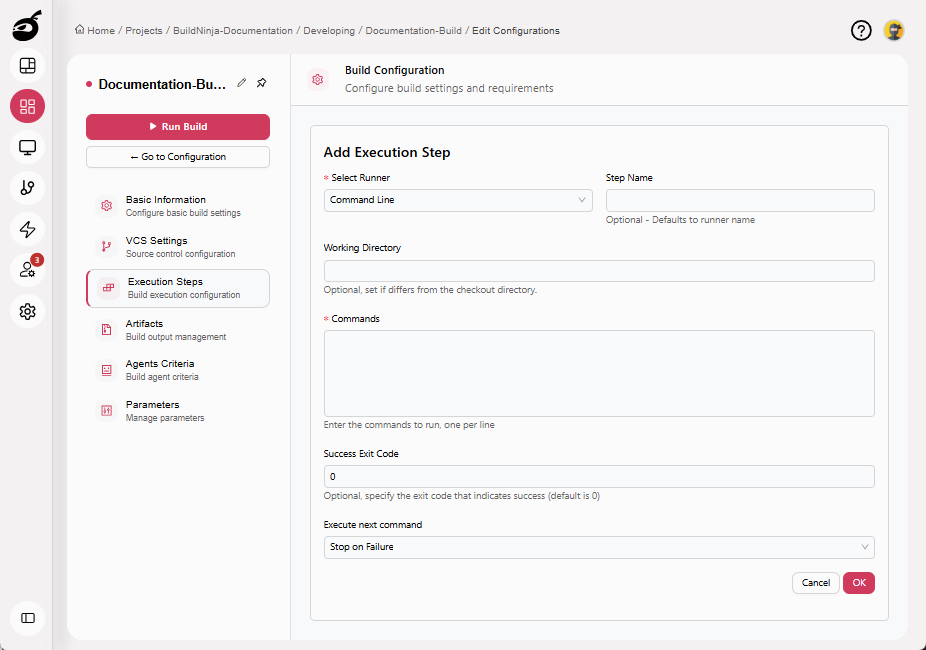
Command LineThe Command Line Runner executes one or more shell or batch commands directly on the BuildNinja agent machine. It provides a flexible way to run command-line tools, scripts, and system utilities, making it well suited fo…: Executes shell or batch scripts; flexible for a wide range of tasks. Parameters include:
- Step Name: Optional step name. Defaults to the runner name if not specified.
- Working Directory: Directory where the commands will be executed. Defaults to the system working directory if left blank.
- Commands: The shell command(s) to run during the build process.
- Success Exit Code: Optional. Specifies the exit code that should be treated as a successful execution. The default success exit code is
0. - Execute Next Command: Controls whether subsequent steps continue to run if this step fails.
-
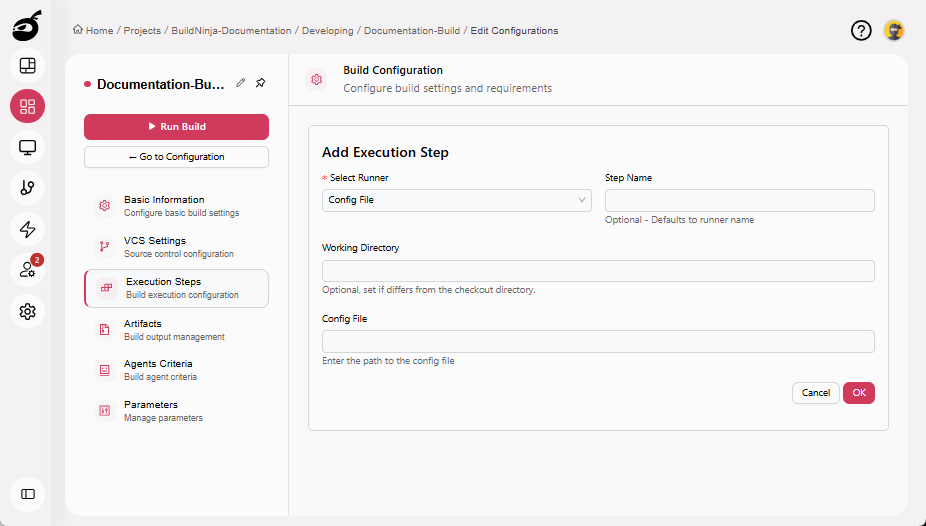
Config FileThe Config File Runner executes builds using a declarative YAML configuration file. It enables build logic to be version-controlled, reviewed, and reused consistently across projects and environments, promoting reproduci…: Triggers and configures builds using a declarative YAML file. Parameters include:
- Step Name: Optional step name. Defaults to the runner name if not specified.
- Working Directory: Directory where the build process runs.
- Config File: Path to the configuration file.
-
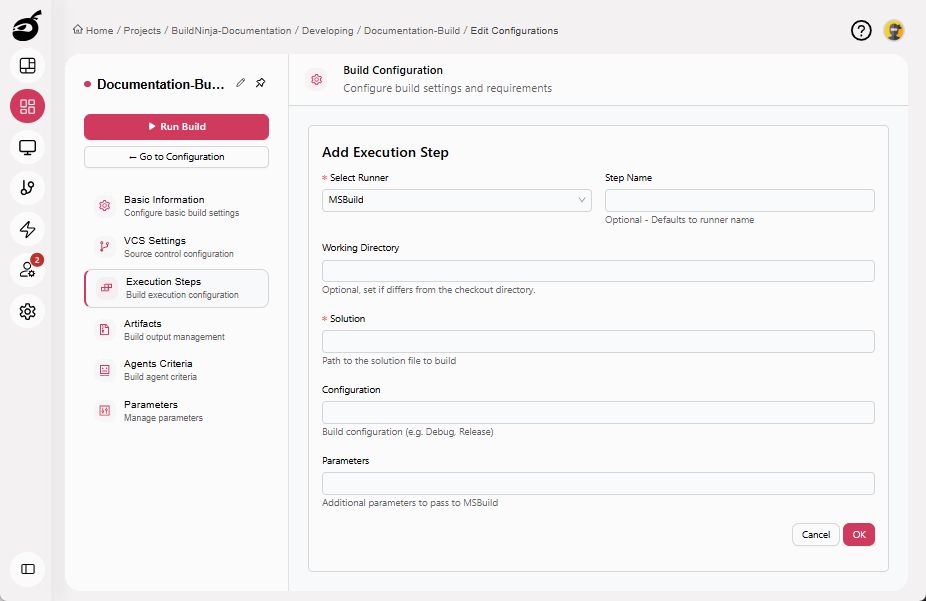
MSBuildThe MSBuild Runner compiles and builds .NET projects and Visual Studio solution files using Microsoft’s MSBuild engine. It provides fine-grained control over build configurations, supports custom parameters, and integrat…: Builds .NET and Visual Studio projects. Parameters include:
- Step Name: Optional step name. Defaults to the runner name if not specified.
- Working Directory: Directory where the build runs.
- Solution: Path to the solution file to build.
- Configuration: Build configuration (e.g., Debug or Release).
- Parameters: Additional parameters to pass to MSBuild.
-
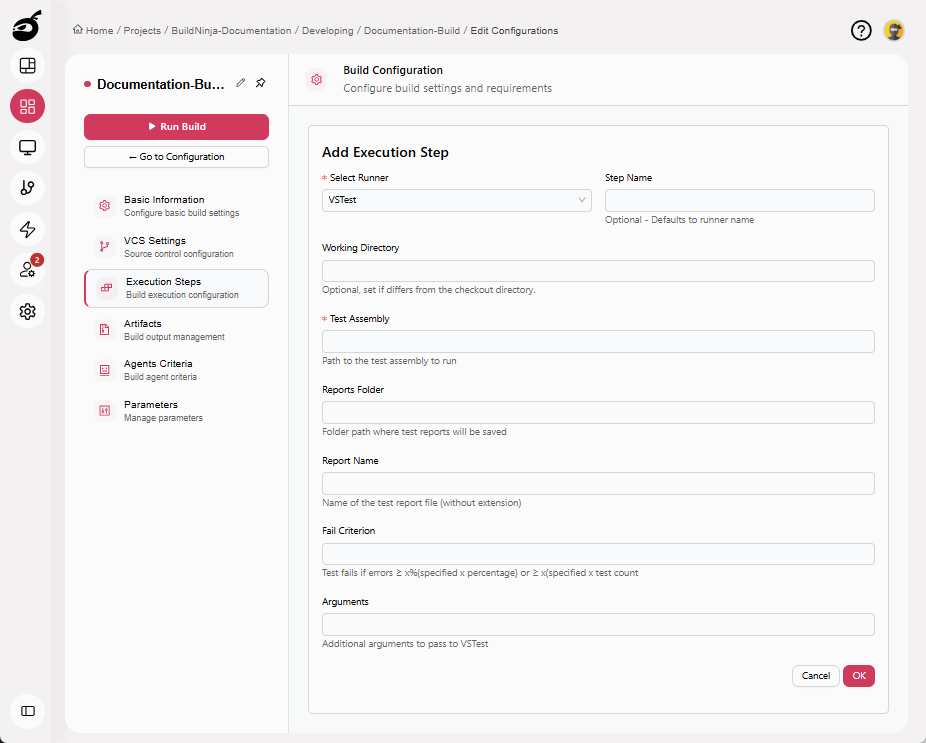
VSTestThe VSTest Runner executes automated tests built with Visual Studio test frameworks and generates structured test reports for analysis and quality validation.: Runs automated tests within Visual Studio projects. Parameters include:
- Step Name: Optional step name. Defaults to the runner name if not specified.
- Working Directory: Directory where the test process runs.
- Test Assembly: Path to the test assembly to run.
- Reports Folder: Folder path where test reports are saved.
- Report Name: Name of the test report file (without extension).
- Fail Criterion: Defines failure conditions — test fails if errors exceed a specified percentage or count.
- Arguments: Additional arguments to pass to VSTest.
-
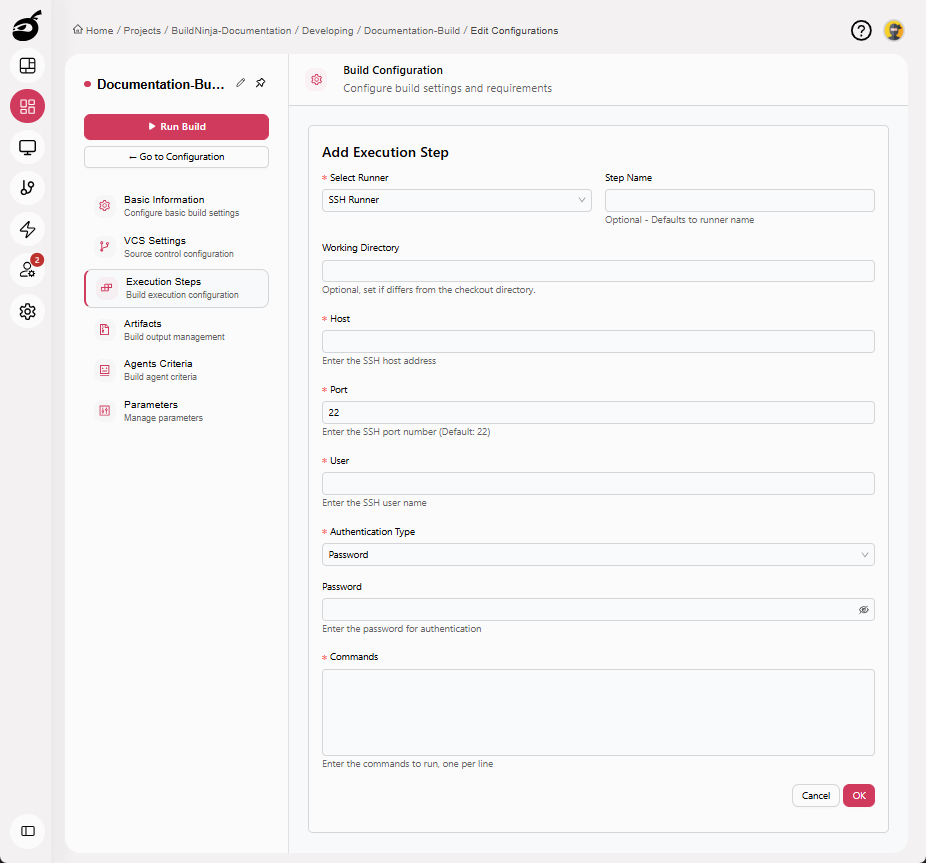
SSHThe SSH Runner executes commands on a remote machine over Secure Shell (SSH). It enables secure remote automation for deployments, infrastructure management, and post-build operations.: Executes commands on a remote machine over SSH, enabling deployments and remote operations. Parameters include:
- Step Name: Optional step name. Defaults to the runner name if not specified.
- Working Directory: Directory where the commands will be executed.
- Host: The SSH host address of the remote machine.
- Port: The SSH port number. Defaults to
22. - User: The SSH user name used to establish the connection.
- Authentication Type: The method used to authenticate with the remote machine. Supported options include:
-
Password: Authenticates using the SSH user’s password. This option is simple to configure but is generally less secure than key-based authentication. This option includes:
- Password: The password used for authentication.
-
Default SSH Key: Uses the default SSH private key available on the BuildNinja agent machine (
~/.ssh/id_rsa) to authenticate with the remote host. This option includes:- Root Password: The password of the remote machine’s root user, used to authorize access if required.
- Passphrase: The passphrase associated with the default SSH private key, if the key is encrypted.
noteThe corresponding public key must be added to the remote machine’s
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile. -
Custom SSH Key: Uses a user-provided SSH private key for authentication. This is useful when a specific key is required for access or when different keys are needed for different environments. This option includes:
- Root Password: The password of the remote machine’s root user, used when privileged access is required.
- SSH Key: The custom SSH private key used to authenticate with the remote host.
- Passphrase: The passphrase associated with the provided SSH private key, if the key is encrypted.
noteThe corresponding public key must be added to the remote machine’s
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile.
-
- Commands: The commands to execute on the remote machine, entered one per line.
-
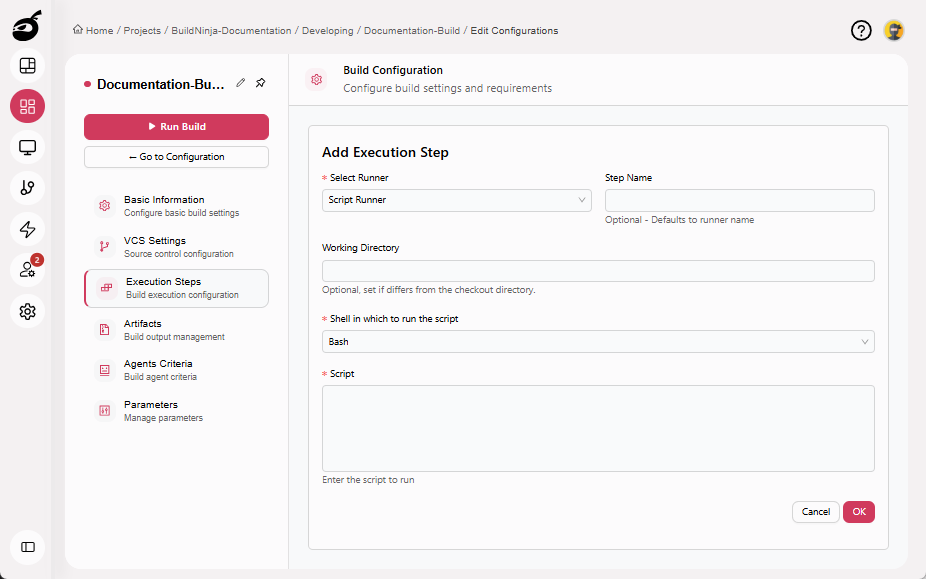
ScriptThe Script Runner executes multi-line scripts using a selected shell or scripting environment. It supports complex logic, conditional execution, loops, and reusable automation, making it suitable for advanced build steps…: Executes multi-line scripts as part of a build step, enabling complex logic, conditional execution, and reusable automation. Parameters include:
- Step Name: Optional step name. Defaults to the runner name if not specified.
- Working Directory: Directory where the script will be executed.
- Shell in Which to Run the Script: The shell or scripting environment used to execute the script. Supported options include:
- Bash: Default shell on most Linux systems; supports advanced scripting features.
- Shell (sh): POSIX-compliant shell with basic scripting support; best for portability.
- Zsh: Feature-rich shell with enhanced scripting and customization (if installed on the agent).
- Command Prompt: Windows command-line interpreter for running
.cmdor.batscripts. - PowerShell: Cross-platform automation shell for Windows-based and cloud workflows.
- PowerShell 7: Modern, cross-platform PowerShell with improved performance and compatibility.
- Script: The script content to execute during the build step. Enter the script directly, using the selected shell syntax.
Agents
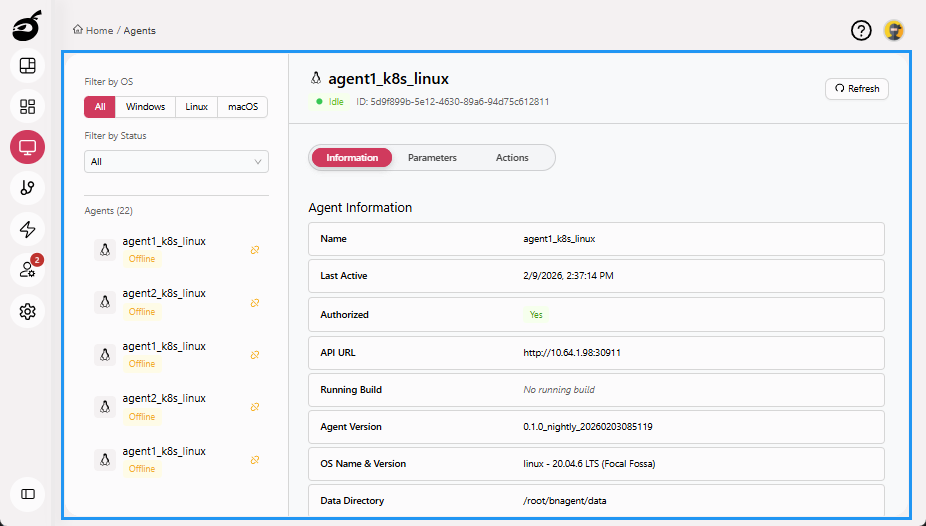
Agents provides visibility and control over the resources that execute builds and deployments. It helps you monitor, register, and manage agents efficiently. Within Agents, you can:
- View a list of all registered agents along with their status
- See key details such as agent name, platform, assigned labels, and current task
- Filter agents based on OS or status
- Enable, disable, refresh, reset, or delete agents
Agent Tabs
The following tabs are available to help you interact with agents:
-
Information: Displays core agent details.
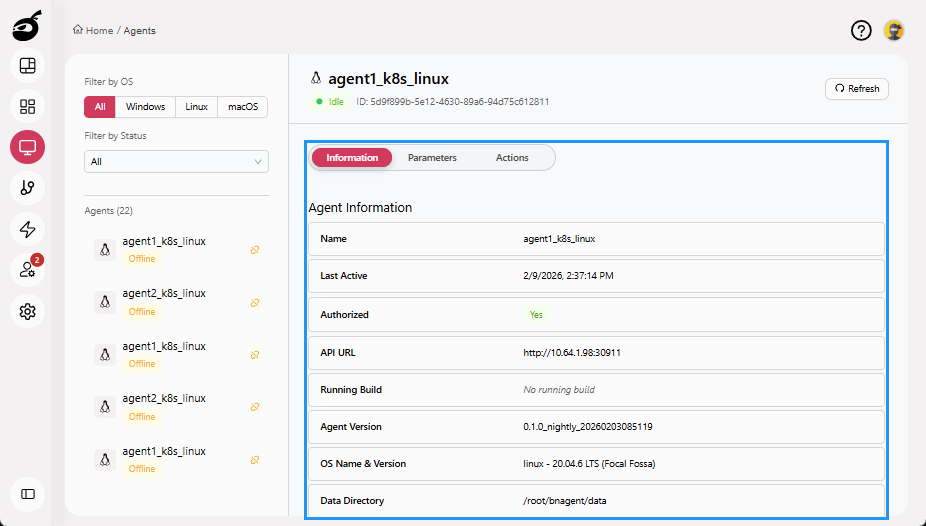
-
Parameters: Shows environment variables associated with the agent.
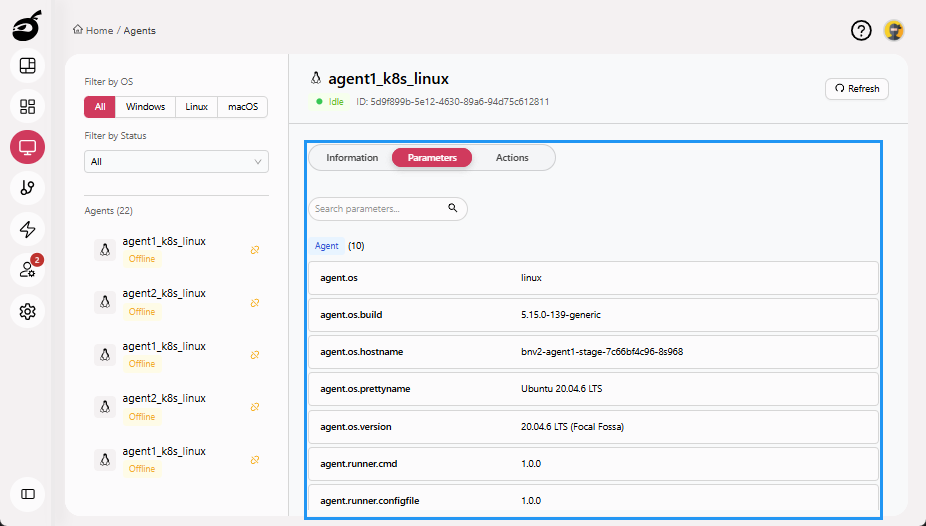
-
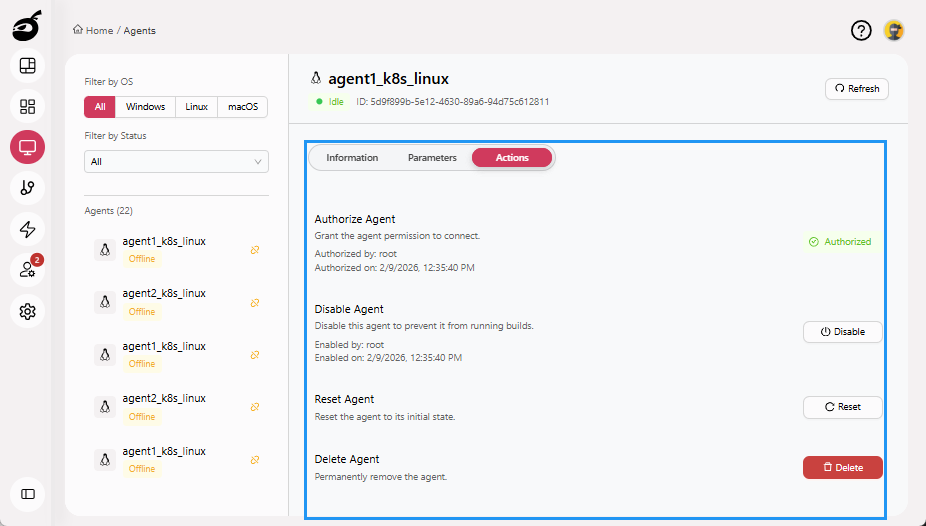
Actions: Provides controls to manage the agent, including authorizing, enabling or disabling, resetting, and deleting.
Queue
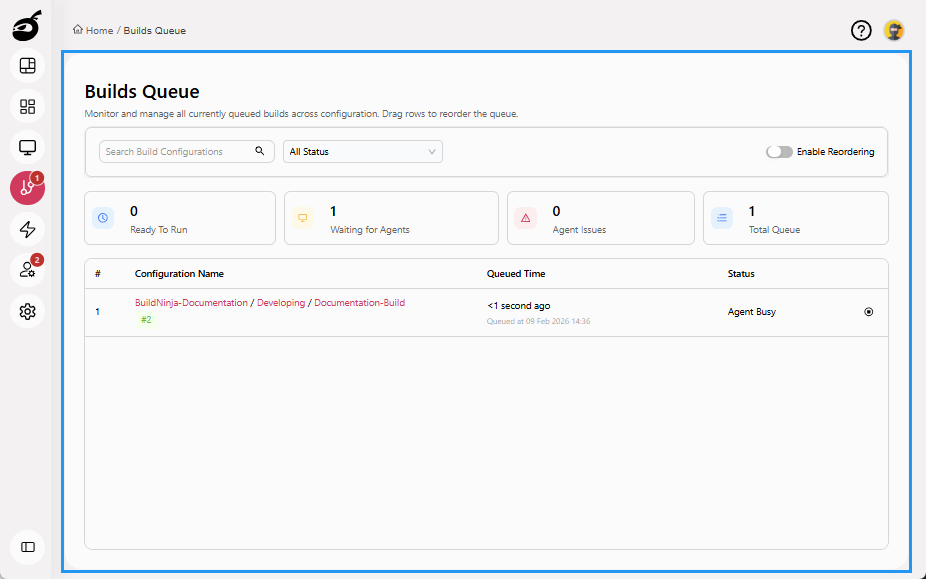
Queue displays and manages builds that are waiting to be executed. It provides you with real-time visibility into the scheduling and prioritization of builds across available agents. Within Queue, you can:
- View a list of queued builds along with their position in the queue
- Identify which build is queued
- Check how long ago each build was added to the queue
- Reorder builds to adjust execution priority
- Cancel queued builds before they start
- Search and filter queued builds to quickly locate specific build configurations
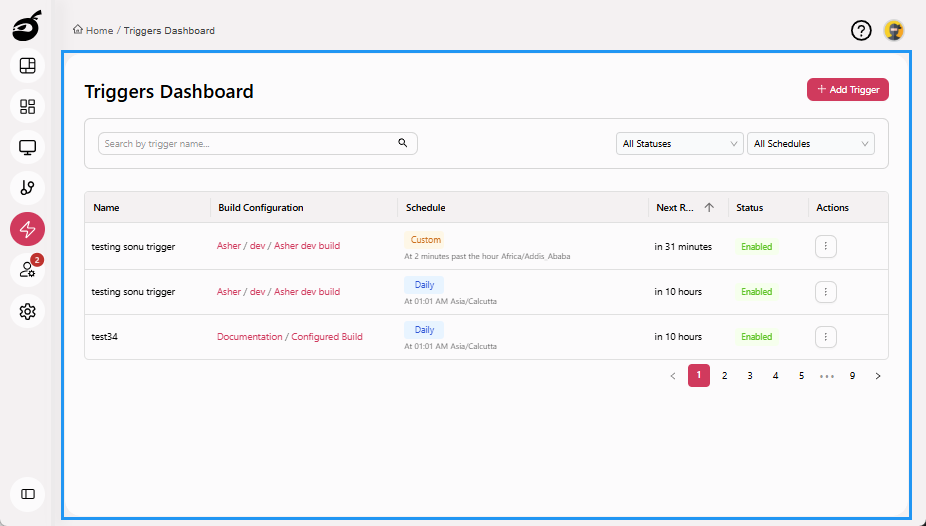
Triggers
Triggers allows you to define and manage the conditions under which a build is automatically started. This helps automate workflows and ensure builds run consistently in response to key events. Within Triggers, you can:
- View a list of all configured triggers
- Add new triggers based on scheduled times
- Enable or disable specific triggers without deleting them
- Search and filter triggers to locate relevant configurations quickly
Build triggers help teams reduce manual effort and ensure timely, automated build execution across development cycles.
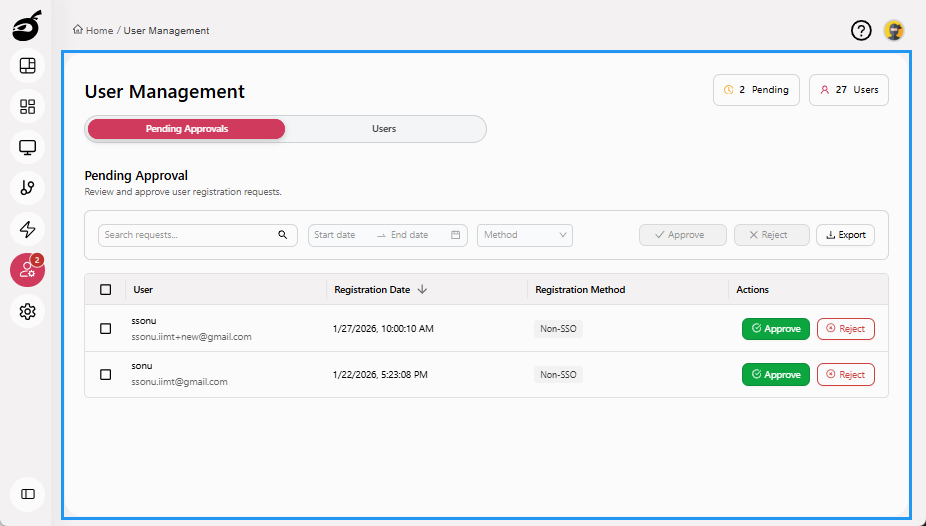
Users
Users provides access to user management and permission settings across the system. It allows administrators to control who can access the platform and manage administrative privileges. Within Users, you can:
- View a list of all registered users along with their status
- Approve or reject user access requests
- Block or unblock users when access is no longer needed
- Grant or revoke System Admin access for users
- Quickly locate users by searching by name or email
- Export a log of registered users and access requests pending approval
Users Tabs
The following tabs are available to help you interact with user-related settings:
-
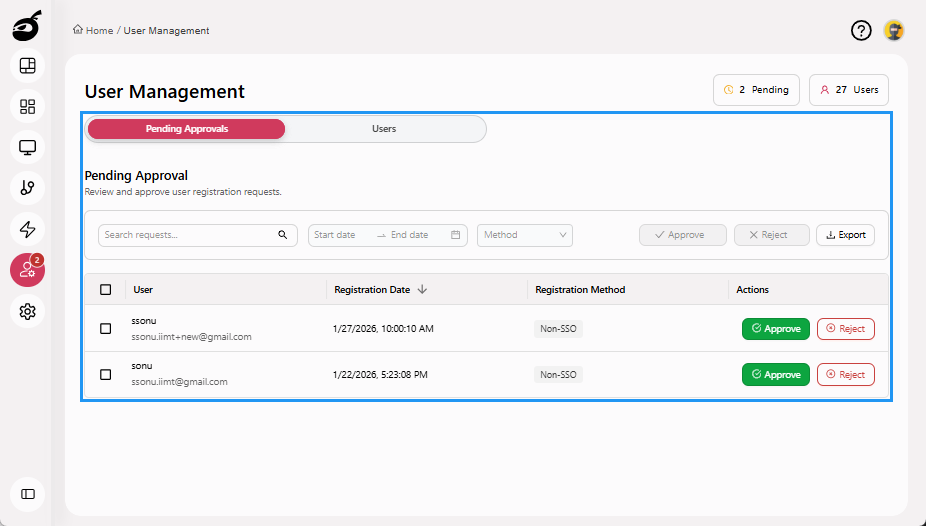
Pending Approvals: Displays a list of users who have requested access, allowing administrators to approve or reject requests. It includes registration date, registration method, and options to search, filter, and export pending requests for record-keeping or audit purposes.
-
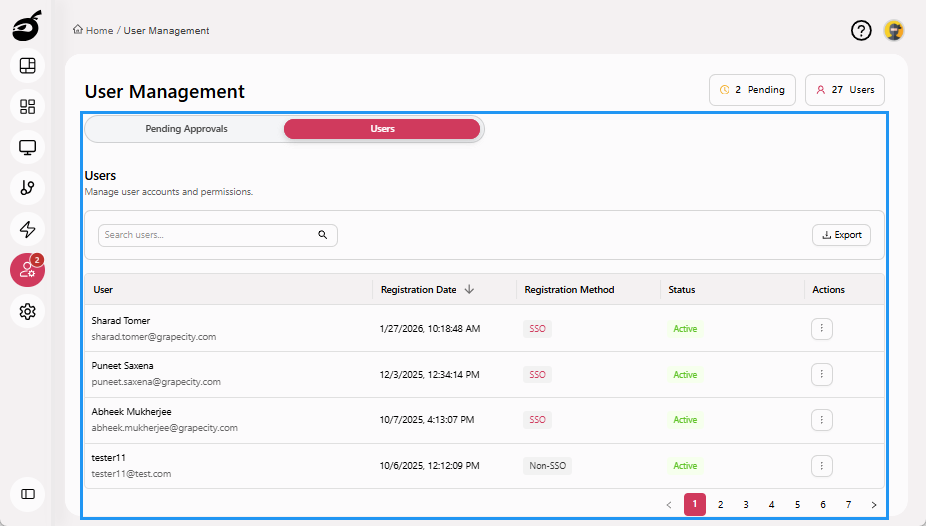
Users: Displays all registered users along with their registration date, registration method, and current status. Administrators can search users, export user records, reset passwords, block or unblock user accounts, and grant or revoke System Admin access for effective system-wide user management.
Settings
Settings provides access to global configuration options that define how the platform behaves system-wide. It allows administrators to manage key settings such as SSO authentication, mail templates, notifier configurations, and license management, ensuring secure, consistent, and centralized platform control.
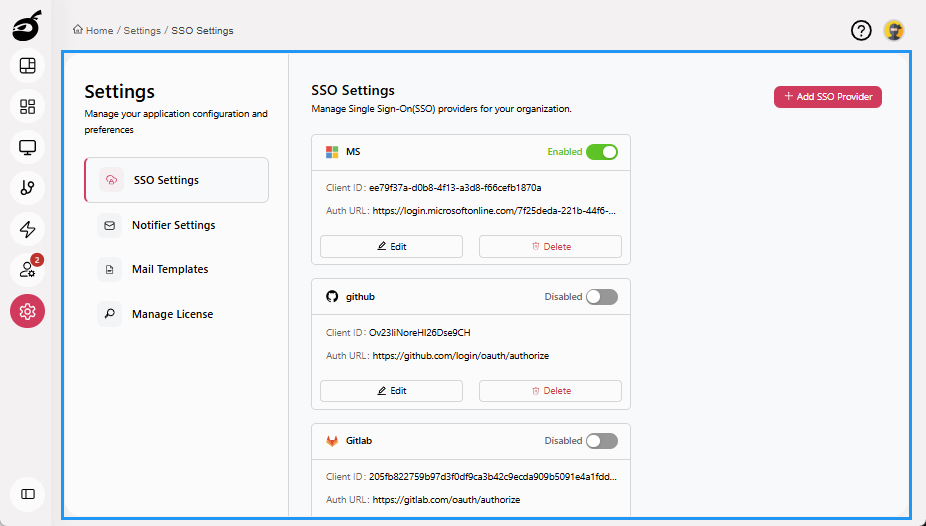
Settings Tabs
The following tabs are available to help you manage key administrator settings:
-
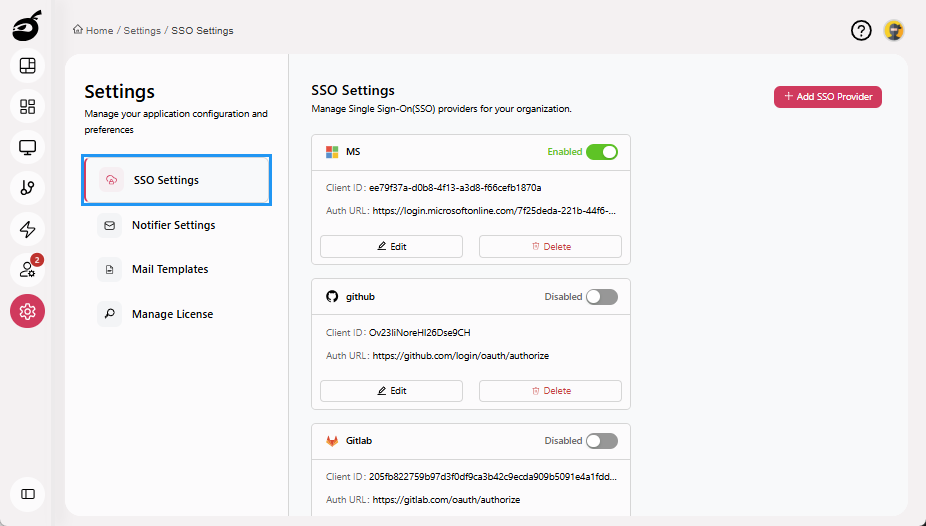
SSO Settings: Configure and manage Single Sign-On (SSO) integration, including authentication providers.
-
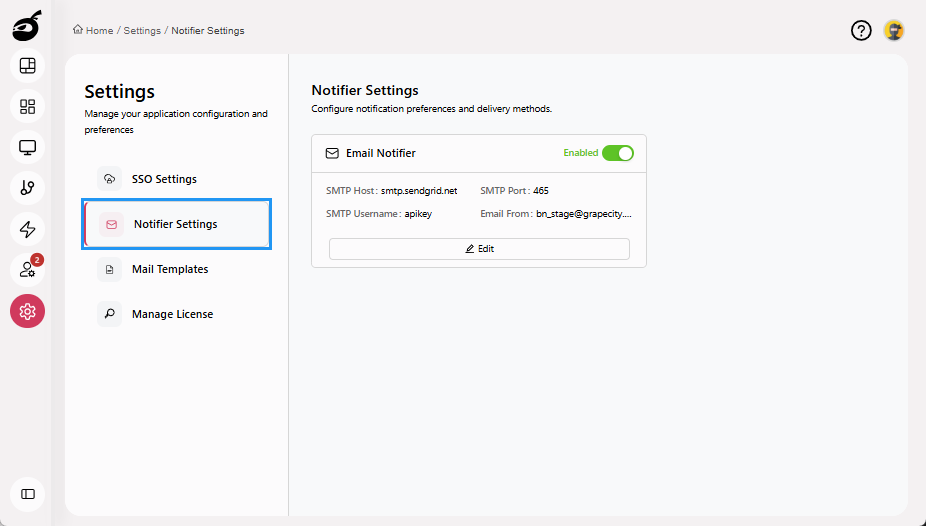
Notifier Settings: Define and manage system-wide notification channels to ensure users receive build and system alerts.
-
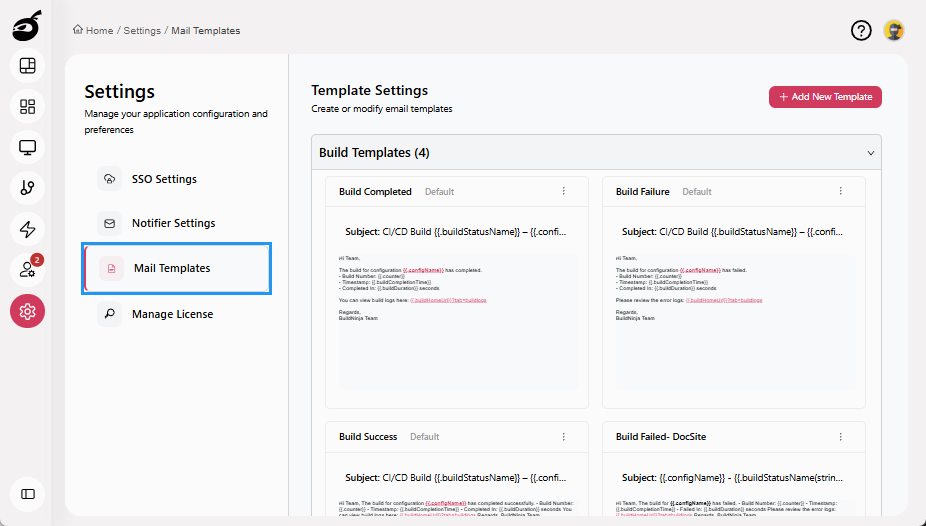
Mail Templates: Create and manage system email templates used for user notifications, approvals, and system alerts.
-
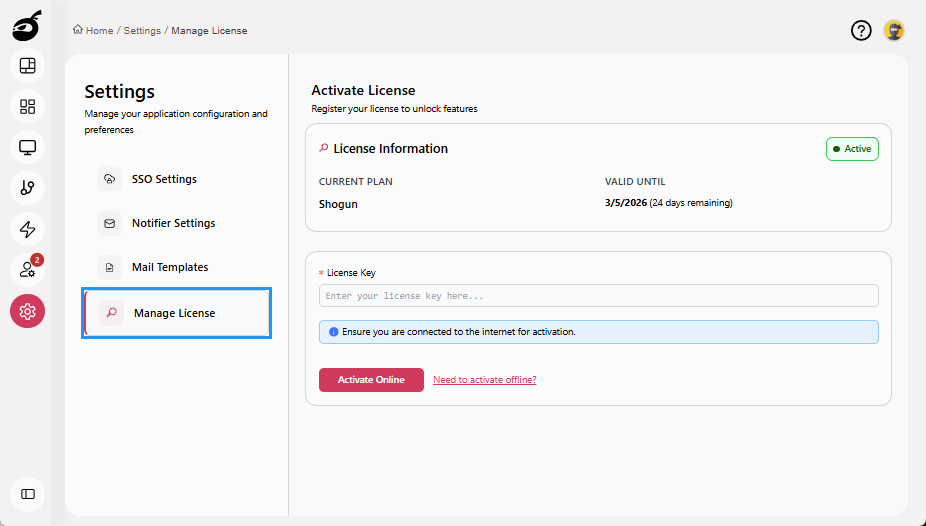
Manage License: View existing license details and add or activate a new license online or offline.
Profile
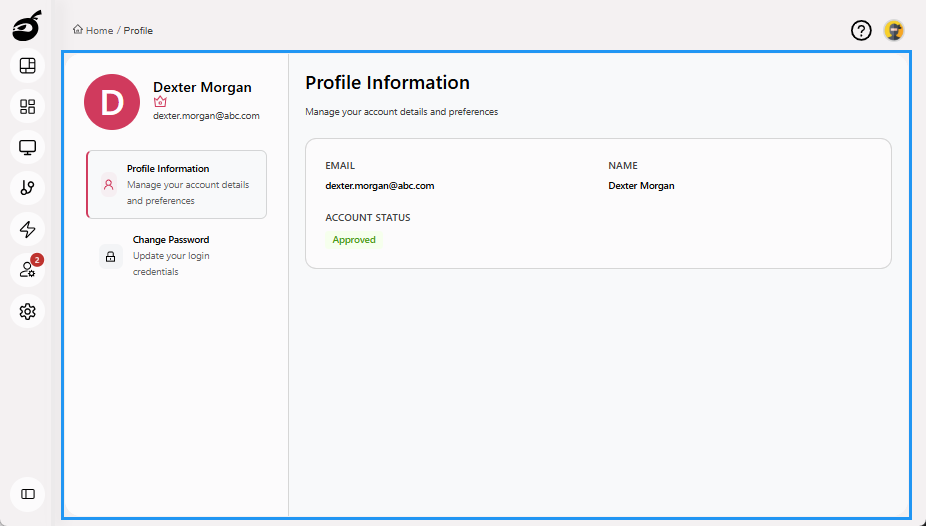
Profile provides access to user-specific information. Manage personal details and update account security settings for your BuildNinja account.
Profile Tabs
The following tabs are available:
-
Profile Information: Displays details about the logged-in user, such as name, email, and account status.
-
Change Password: Allows you to update your account password securely.